Difference between PVC and SEBS
Thermoplastics > Styrenics

| PVC vs. SEBS medical industry | ||||||||
| Challenges in medical applications | ||||||||
During the last year s, regulatory and market drivers and cost pressures have continued to generate a discussion of the choice of material between the polyvinyl chloride (PVC), thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) and rubber materials . Health systems are applying pressure and are already implementing strategic initiatives for patients without phthalates environments. TPEs are being viewed as a replacement for PVC in applications where phthalate - free plasticizers or materials are required. R ecently, TPEs have also been used to improve suavedad, and rgonomía, protection and / or function. L os producers of intravenous therapy are the firstenvolucrado medical device to transition to PVC TPE materials. TPEs are also replacing the thermoset rubbers (such as silicone, polyisoprene and butyl rubber) used in elastomer physician, complications such as septa, caps and syringe plungers l os drivers for replacing rubber are improved processing, cost and ff ectiv eness and removable low. |  | |||||||
| Alternative to PVC | ||||||||
There are two main reasons for sostituir PVC. First, plasticized PVC has an undesired related to the release of dioxins when incinerated uncontrolled environmental impact. Secondly, there is concern that plasticizers of PVC (called "estrogen mimics") can migrate to the human body. Potential alternative plasticized PVC tubes are polymer compositions containing polypropylene (PP) combined with a copolymer of elastomeric blocks. These compositions do not contain "estrogen mimics" or release dioxins when incinerated. SBCs are thermoplastic elastomers consisting of polystyrene end blocks (PS) chemically linked by a connecting rubber block PB. The rubber intermediate block consists most frequently PB polybutadiene, polyisoprene IR or hydrogenated versions poly-olefin: ethylene-butylene and ethylene-propylene SEEPS. | ||||||||
| New family of hydrogenated SBC | ||||||||
A new family of hydrogenated SBC appears to be closing the performance gap with plasticized PVC. This family is based on midblock segment improved rubber (ERS), containing a higher content than more traditional butylene midblock SEBS. The benefits of ERS-SEBS polymers include improved processability and better compatibility with polypropylene. The fine network of ERS-SEBS mixture leads to a significant improvement in transparency. Another effect of improved compatibility with PP is a broadening of the glass transition temperature (Tg) below room temperature. The improved compatibility opens a number of properties of the material, which makes the SBC-PP mixtures are very suitable for replacement of plasticized PVC. Binding to these new materials can be challenging due to lack of bondable molecules along the polymer surface. A light curable adhesive provides high adhesion to all the various components. |  | |||||||
| Morphology | ||||||||
The morphology of styrenic block copolymers can be described best by the domain theory. Usually the elastomer is the main constituent, the block copolymers have a similar morphology to that shown in the figure, where the end segments of polystyrene spheroidal form separate regions, ie, domains dispersed within a continuous phase. At room temperature, these are hard polystyrene domains act as physical crosslinks and, connecting the elastomeric means in a 3D network segments. In some ways, this is similar to network domains formed during the vulcanizing conventional rubbers using sulfur cross links. | 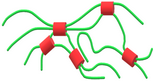 | |||||||
| TPE-S, TPS, SBS, S-B-S | TPE-S, TPS, SEBS, S-E-B-S | |||||||
| Dominio duro = PS Poliestireno Dominio duro = Polibutadieno PB | Dominio duro = PS Poliestireno Dominio duro = Poli (etileno-co-butileno) EB | |||||||
| TPE-S, TPS, SIS, S-I-S | TPE-S, TPS, SEPS, S-E-P-S | |||||||
Dominio duro = PS Poliestireno Dominio duro = Polisopreno IR | Dominio duro = PS Poliestireno Dominio duro = Poli (etileno-co-propileno) EP | |||||||
| TPE-S, TPS, SEEPS, S-E-E-P-S | Properties | |||||||
Dominio duro = PS Poliestireno Dominio duro = Poli (etileno-etileno-co-propileno) EEP |
| |||||||
| Structure | ||||||||
Since the rubber blocks and hard polystyrene are incompatible, a strong phase separation results in the formation of polystyrene domains. These domains act as physical cross and can rupture and reset by a combination of shear and temperature links. The amount of shear required to process SBC depends on molecular weight of polystyrene (Mw) and the type of rubber midblock. Styrene-ethylene-butylene-styrene (SEBS) SBCs are usually not hydrogenated his predecessors strongest domains. Styrene compounds TPE-S. The styrenic block copolymers, polymers based TPE-S, are exceptionally versatile polymers and are themselves a thermoplastic elastomer material, but are not considered final products.Block copolymers of styrene are based on simple molecular structures, such as a copolymer of SES blocks, where S is a polystyrene segment and E is a segment of elastomer and differ by the molecular weight, the percentage of styrene content (PSC ) and the type and length of elastomeric midblock. The development of chemistry styrene block copolymer, has led to improvements in compatibility and clarity with polypropylene, and the ability to formulate soft compounds without the use of mineral oils or plasticizers. This has allowed the TPE-S compounds directed to medical device applications where traditionally used PVC compounds. |  | |||||||
| Propiedades Físico-Mecánicas | ||||||||
SEBS styrenic block copolymer elastomers are some of the most versatile and easy to process materials in the plastics industry. The XPRENE EB offers an excellent coefficient of surface friction, low permanent deformation, high tensile strength. Normally they do not require drying, they have wide processing latitudes and they have good to excellent thermal stability. Most commercial TPEs can be processed by a variety of techniques. In addition, there are many specialty degrees formulated to adapt to particular processes. Other features include neutral base color, resistance to aging and UV radiation, compression adjustment and food contact approval. Special qualities with specific acoustic properties, modified adhesion, higher thermal resistance and flame retardancy complete the current range of products. | ||||||||
Physica and mechanical properties | ||||||||
| The glass transition temperature (Tg) of the polybutadiene blocks is typically -90 ° C, while the Tg of the polystyrene blocks is + 100 ° C. Therefore, at any temperature between -90 ° C and + 100 ° C, SEBS act as an elastomer physically crosslinked. The operating temperature is guaranteed from -40 ° C to + 100 ° C. | ||||||||
Electrical Properties | ||||||||
SEBS are typically good insulators with high relative electrical resistivity being nonpolar polar best. However, the electrical properties of the compounds of XPRENE EB are more dependent on the ingredients used in the formulation of the elastomer base. We antistatic compound SEBS and even conductive by the incorporation of sufficient amounts of graphite, special types of carbon black, certain metal powders or polar products in the rubber mixture. However, the conductivity obtained by these means does not resemble that of metals. | ||||||||
Optical properties | ||||||||
| One of the features of a two-phase system is that light is scattered when passing from one phase to another, resulting in different levels of transmission of light, in the case of SEBS also have transparent degrees. | ||||||||
Chemical properties | ||||||||
Unlike SBS, SEBS contains no double bonds (which by nature are sensitive to oxidation), which makes it particularly resistant to wear. Therefore, it is ideal for extreme conditions having to do with heat, ultraviolet radiation, ozone or oxidizing agents. SEBS well resist stress crack (stress cracking) acid, hydroxides, methanol and ethanol, absorb oil, fats, aliphatic hydrocarbons. Instead they not resist polar hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, carboxylic acid, gasoline, oil ASTM No 1 Paraffin, ASTM # 3 oil Aromatic, toluene and benzene. | ||||||||
Processability | ||||||||
The SEBS belong to the class of thermoplastic elastomers having the mechanical properties of rubber at room temperature and thermoplastic processing capabilities. The SEBS are rubbery without being crosslinked, so it is easy to process to achieve useful forms, usualente is processed more or less at 150-230 ° C. L os Sebss may have different characteristics, mainly highlighting its versatility for bi-injection molding or plastic materials. They can be processed with various methods such as injection molding, extrusion or blowing. In addition, XPRENE EB has been specially created for marketing demands and meet customer requirements. Doesn't release chloridric acid as the PVC during the injection mold. | ||||||||
| Overmolding 2K | ||||||||
TPEs are ideal for overmolding provides a softer feel and improved ergonomics (like grip) for a variety of tools and surgical devices. This can improve instrument control and reduce fatigue during long procedures for medical professionals. Adhesion to a wide range of polar and nonpolar substrates such as PP, PA, ABS, PC, PS, SAN, ASA, PBT, PET, ABS / PC etc. For the selection process overmolding in certain TPEs can vary the strength of binding in the application, for example if the molding process is chosen for multi shot (multi-shot) compared to the insert molding, the first promotes certain greater bonding force or binding because the two materials melt upon binding,while the second gives a poor bond since one of the two materials (plastic) is superimposed on the other that is not cast (metal). So the selection process to be applied is a key to produce a high quality factor. Within the choice of material depends on the company and product handling, where one has to consider the characteristics of each material for the application of overmolded, as there are a variety of materials having different properties that provide softness, texture, adhesion, and wall thickness of the material. For the effect of the thickness it is necessary to know the hardness of the material,example when TPE material has a low thickness (typically> 1mm) is perceived harder and vice versa when having a thickness greater than 1 mm will feel smooth. To ensure a good link overmolding their searches a thickness in the range 1.5mm for most applications overmolding. |  | |||||||
| Compound | ||||||||
Functional compounds of TPE-S are created by combining styrenic block copolymers with a number of selected additives (such as PP, PE, mineral oil, lubricants or antioxidants) for the mixture of compounds. This is generally known as a compound TPE-S.Including a filler to a polymeric matrix can describe a compatibilization effect between immiscible or poorly miscible blends exhibit excellent and well electrical conductivity, hardness, stiffness, mechanical and thermal resistance, and even reach confer bactericidal properties to new material. Melt blending of polymers has been the fast track to the design of new resins that seek to combine the properties of Y SEBE PP to reach the superiority of certain features because of the synergy that may occur. Unlike SBS, SEBS contains no double bonds (which by nature are sensitive to oxidation), which makes it particularly resistant to wear. |  | |||||||
Others Proprierties | ||||||||
| ||||||||
Applications | ||||||||
Typical applications are, profiles, housewares, handles, knives, handles, fittings, feet, storage, slip inserts, knobs, buttons, seals, profiles, covers pedal, power tools, seals for cables , plugs and sockets, wire coatings, switches, enclosures, garden tools, knobs, dampers, fins, masks, caps, terminals, slip. SEBS is already used in the production of toys and can replace PVC for producing doll heads (with hair) using rotational molding techniques, one of the most difficult PVC substitutions. The SEBS is also used in the electrical industry for articles such as flexible cables can replace PVC. The high performance polymers are often selected for applications requiring retention of structural and dimensional integrity upon exposure to aggressive chemical conditions and high temperatures. One of these options is cost-effective performance polymers plasticized PVC. However, much attention has been paid to assessing polymers safer for the environment and biological. Gums styrene-ethylene-butylene-styrene (SEBS), SEBS blends / polypropylene, TPE (thermoplastic elastomers) and polypropylenes are emerging as alternative high performance. In particular, TPEs are used to replace plasticized PVC low durometer medical device applications where biocompatibility characteristics are crucial. But nevertheless, SEBS is used as a possible replacement of PVC in the manufacture of toys. SEBS is similar to natural rubber and is less dangerous compared to their counterparts. FDA approvals and BGW for implementing SEBS can create an opportunity for growth for the product in the global market. The styrene polymer SEBS styrene used as the central building block, and has favorable properties, such as improved impact resistance, flow, rigidity, low temperature, thermal stability and durability. SEBS is now replacing PVC, due to its greater structural retention, dimensional integrity and chemical compatibility. In addition, SEBS, being free of phthalates and environmentally friendly, can replace the application of PVC in multiple industries. SEBS has been replacing the application of PVC in industries such as medical, pharmaceutical, adhesives and sealants, cables and wires, building materials, cosmetics and personal care, agriculture, packaging, footwear, furniture, clothing, toys, sports and electronic items. Using SEBS gadgets is increasing in the manufacture of medical devices, tubes and bags, as it is biocompatible and comparatively environmentally friendly than PVC. | ||||||||
