Policarbonate - PC
|
PC products range
|
|
|
We have more than 20 different types of polycarbonate resin, many of these contain aggregates to improve the original properties of polycarbonate for a certain application, such as: fiberglass, UV absorbers, anti-flame additives (we have compliance with UL94, V0, 5VA) and other specifications and includes products that can be used in applications that have to meet the requirements of halogen-free parts, mold release agents, antioxidants, etc. All these materials can be marketed in transparent "color" (except materials with fiber and some anti-flame) or in translucent (ditto) and opaque colors. We have a wide versatility of design through its extensive range of viscosities and product options, such as: respect for the environment for its resistance to scratching, hardness, heat resistance, weather resistance, bio-compatibility, optical quality We also have resins Special when food approval characteristics are required and compliance with the strict requirements of the FDA, USP and Class VI.
|
| 
|
Policarbonate - PC
|
|
|
Polycarbonates are a particular type of polyesters, long chain polymers, formed by functional groups connected by carbonate groups (-O- (C = O) -O-). Because the benzene groups are directly in the main chain, the molecule is very rigid, causing the polycarbonate to have an amorphous structure, a low contraction in the molding (both transverse and parallel to the flow) and be transparent. The exceptional resistance to shock of polycarbonates, together with its perfect transparency, explains its use in anti-bullet glazing of premises, in horticultural greenhouses where they endure the most severe hail storms, in automobile headlights or compact discs. Thermoplastic with little tendency to crystallize with very little absorption by water. It has a high refractive index and a good transmission of light in the visible region. Thermoplastic with little tendency to crystallize with very little absorption by water. Its density varies between 1.20 and 1.24 g / cm3.
| |
|
Symbols
| Formula |
|
|
- PC
- Policarbonato
- Polycarbonate
- Formula bruta: (O-(C6H4)-C(CH3)2-(C6H4)-CO
- Número de registro CAS 25037-45-0
| 
|
| PC properties |
|
|
|
- Good impact resistance
- Good resistance to sterilizable temperature
- Good dimensional stability
- Good dielectric properties
- Low combustibility
- It is stable against water and acids
- Good electrical insulation
- It is not biodegradable
|
| | 

|
PC Physica and mechanical properties |
|
|
Although the main structure of the polycarbonate chain is frozen at room temperature, thanks to its phenylene, isopropylidene and carbonate groups, it has sufficient mobility to dissipate impact energy at room temperature. Mechanically it is a plastic that has great hardness. According to the Rockwell hardness tests by the UNE-EN ISO 2039-2: 200 standard, the polycarbonate resin has a hardness in the M scale of 75. It is also very resistant to traction, compression and especially impact; and even breaking it has a great resistance to fragmentation. Despite this great resistance, it scratches very easily and its scratching is not easy to repair. It is 300 times stronger than glass and 30 times stronger than acrylic. With what it offers a margin of security that does not give any other material designed for encristalado.
|
| 
|
PC Thermal properties |
|
|
The mobility of these lateral groups ceases at lower temperatures (alpha = 0ºC and beta = -200ºC), causing the impact resistance to fall. It has the advantage that it is a material that is difficult to burn or fireproof and can also be dyed in opaque and transparent colors. Its regularity and the polar lateral groups offer a high value of the glass transition temperature Tg to polycarbonate (145ºC), this makes it possess high values of thermal properties, and very good dimensional stability. Good thermal insulation. It is a material that burns with difficulty because it is self-extinguishing. When it burns, it decomposes forming a thick smoke.
|
| 
|
| PC Optical Properties |
|
|
It is transparent but not as bright as PMMA, Methacrylate, it has an index refractive elevation and a good transmission of light in the visible region. It tends to yellow after long exposures to UV light. If the exposure to UV rays is intense, it should be protected with UV additives. The IR spectrum has been made from absorbance measurements. Two signals appear at 2968 cm-1 and 2928 cm-1 corresponding to the Stretching of the CH sp3.In 1768 cm-1 appears the carbonyl signal C = O. The peaks corresponding to 1221cm-1, 1186cm-1 and 1153cm -1 correspond to the asymmetric stretching CO.
At 1409cm-1 the asymmetric deformation vibration of the CH3 groups appears while the symmetric deformation of the C (CH3) 2 is at 1368cm-1. Between 2000 and 1650cm-1, very weak combination bands of the polymer phenyl groups appear. At 1077cm-1 and 1008cm-1 appear under the deformation vibration bands of the CH of the phenyl group; the vibration is in the plane. The peaks corresponding to 884, 823 and 759cm-1 correspond to the deformation bands of the same CH, but the vibration is outside the plane.
|
| 
|
PC Electricas and Acoustic Properties
|
|
|
Good electrical insulation, regardless of the moisture content and the ambient temperature. It is electrical insulator unlike glass which is considered a semiconductor whose resistivity decreases rapidly as the temperature increases. Saving electricity and contributing to the obtaining of LEED credits. Acoustic insulation (4mm thick): 27 dB
|
| 
|
| PC Chemical properties |
|
|
The chemical properties of thermoplastic polycarbonate are those of a slightly polar polymer. The carbonate groups are extremely sensitive to hydrolysis and, as they are in the main chain, can cause degradation in the properties of the thermoplastic. Due to this reaction the polycarbonate must always be dry for the process, otherwise the material would see its molecular weight drastically reduced and the properties and appearance deteriorated. Generally the polycarbonate is not sensitive to organic and inorganic acids under normal conditions of temperature and concentration, however its resistance to other organic compounds is low. This low resistance is even more affected with the appearance of micro-fissuring over tension, which causes porosity in the surface of the material, facilitating the chemical attack. In the presence of carbon tetrachloride appears the phenomenon of tension-cracking. As for the ignition, it is a flammable material. It has very good resistance to the presence of fresh and salt water. It has a good resistance to UV radiation from sunlight.
|
|
 |
| PC Processability |
|
|
The artifacts in the PC pellets are generally made by injection molding, blow molding and extrusion, and can then be processed with the standard equipment for carpentry and metallurgy without suffering cracks, pitting, breakage of any kind. The films and fibers are produced by extrusion or solution. The first can be subsequently thermoformed, and like the other PC stick semi-easily made with epoxy adhesives and ultrasonic welding.
| |

|
| PC welding |
|
|
It is advisable to dry the piece first. Once welded with hot gas, it must be annealed. It is better to weld with hot elements, friction or ultrasound. It is highly weldable.
|
| 
|
PC Engineering Notes
|
|
|
Polycarbonate PC polymer is machined grade, it is not optically clear. It can be mechanically or steam polished to improve optical clarity. Caution: during machining, never use refrigerant with aromatic base.
|
| 
|
| Polimerization PC |
|
|
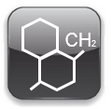
Polycarbonates are similar to polyesters, but their carbonyl group is bonded to two groups is prepared from diphenyl carbonate and a dienol called bisphenol.
|
| 
|
| PC Applications |
|
|
Polycarbonate is a material that allows its use in countless applications. As we have seen its properties of transparency, impact resistance and its ability to withstand temperatures of up to 130 ° C, are common to all varieties of polycarbonate. The polymer PC is used as a basis for photographic films, on screens, a helmet and safety glasses, in lenses for glasses; electric diffusion covers, flight components, lighting systems, laminated sheets for bulletproof glass, moons and headlights for cars, lenses for glasses, solar collectors, furniture and kitchen utensils, utensils suitable for microwaves, sterilization of medical components , compact disc (CD), plates, tubes, sheets, optical fibers, plugs, coffee machines, filters, canteens, slide frames, pens, parts for office machines, cameras, projectors, photometers, binoculars, watches, supports optical computer memory. Polycarbonate is the most suitable material to replace glass in many applications, which represents an important weight saving, because polycarbonate is much lighter than glass. In addition, polycarbonate can take curved shapes very easily, can be in transparent or opaque colors and in case of breakage, it does not occur in a fragile way bursting into a thousand pieces.
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|

