PS
Thermoplastics > Styrenics

Polystyrene PS | ||||||||
Products range (XSTIR) | ||||||||
At Mexpolimeros we offer a wide range of polystyrene resin and its compounds developed according to your needs, guaranteeing quality in products and service. Our range of products includes grades without reinforcement, with fiberglass and / or with mineral load (Ibridos), loaded with metals, with special additives such as heat stabilizer, UV, metals, antistatic, antibacterial, laser marking, nucleate etc, lubricant Special and flame retardant (with or without halogens). We are also developed and evaluated by highly qualified personnel with advanced technology. |  | |||||||
PS - styrene and acrylonitrile copolymer | ||||||||
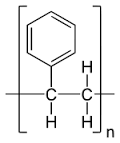
It is an aromatic synthetic polymer made from styrene monomer, (CH2-CHC6H5-) n. The chemical structure of polystyrene comprises only carbon and hydrogen atoms and is classified as hydrocarbon. The carbon atoms are linked together by covalent bonds and each alternative atom of the chain has a phenyl group attached of which it forms a long chain hydrocarbon. Polystyrene is produced by the polymerization of the stirene monomer. There is a distinction between atactic polystyrene and syndiotactic polystyrene, atactic polystyrene is amorphous and transparent also called crystal polystyrene, while syndiotactic polystyrene has a semicrystalline polystyrene. The structure is a relatively rigid polymer, the atactic polystyrene has a density of 1050 kg / m3. It is a very cheap resin per unit of weight. It has a low barrier to oxygen and water vapor and has a relatively low melting point. Polystyrene is easily expandable, once expanded it takes the acronym EPS, commonly known as expanded polystyrene is composed of carbon, hydrogen and 98% air. Expanded polystyrene is obtained by the polymerization of styrene that occurs in the form of small transparent beads. The latter expand up to 20-50 times its initial volume thanks to contact with pentane (gaseous hydrocarbon) and water vapor at 90 ° C. Inside the pearls is formed a closed cell structure that traps the air from which the excellent characteristics of the EPS used as thermal insulation, is an excellent electrical insulator for the capacitors, and is practically anigroscopic. A prerogative that makes it extremely versatile is the ease with which it can be colored, either with bright or matte colors. | ||||||||
Symbols | Formula | |||||||
|  | |||||||
| PS Properties | ||||||||
| ||||||||
| PS Physical and mechanical properties | ||||||||
The structural unit of the polystyrene molecular chain, [-CH2-CH (C6H5) -] n, consists of two vinyl groups and a lateral phenyl group. The specific position of the benzene ring is, however, sufficiently random to inhibit crystallization. The lateral group of great molecular weight makes it difficult to organize the chains and therefore the material is essentially amorphous. Polystyrene softens when heated above its glass transition temperature. The crystalline form of polystyrene has a low impact resistance. Polystyrene degrades due to exposure to sunlight due to photo-oxidation, which reduces its mechanical properties. With the addition of polybutadiene, polystyrene resistant to HIPS is obtained. | ||||||||
| PS combustion test | ||||||||
| When we perform combustion tests on the copolymers of styrene and acrylonitrile, we see a behavior that causes quite a few ashes arranged in flakes, being yellow in color as the flame is concerned. The characteristic smell of burning SAN is characteristic styrene smell, together with hydrochloric acid. | ||||||||
| PS Electrical properties | ||||||||
| They depend on the percentage of water absorbed, good capacity as electrical insulator, good surface resistance and therefore good resistance to slip currents. They have dielectric losses at high frequencies, but excellent use at low frequencies. They have an electrostatic charge (attracts dust) | ||||||||
| PS Thermal properties | ||||||||
Due to the stiffness of the molecular chain of the PS resin, due to the effect of the benzene ring, the glass transition temperatures (Tg) of the commercial materials are in the range of 90-100 ° C. As a consequence of this value of the Tg and added to the amorphous nature of the polymer, at room temperature there is a material that is hard, rigid and transparent. However, above its Tg the polymer PS subjected to stress behaves like a viscous liquid. | ||||||||
| Optical properties PS | ||||||||
Is styrene UV resistant? It has little resistance to oxygen and UV rays, and is quite fragile. The PS pellets is very transparent and has a beautiful shiny finish. The additional scratch resistance makes it a suitable choice for displays at the point of sale and cosmetic items. | ||||||||
| PS Chemical resistance | ||||||||
| The PS polymer, generally good although it depends on the grade of the resin, the chemical concentration, temperature and stress on the parts. It is resistant to oils, fats, formaldehyde, gasolines and hydrochloric acid. Furthermore, it is not attacked by water chemically speaking. | ||||||||
| PS Processability | ||||||||
PS granules can be easily molded by means of injection, extrusion, spalling, molding or using the rotation system. The high impact is more difficult because having a higher rubber content makes them more viscous. Its characteristics are similar to those of non-ferrous metals, can be drilled, milled, turned, sawed and die cut. | ||||||||
| PS Polimerizaction | ||||||||
The addition polymerization of styrene occurs spontaneously even if it is very slow at room temperature if the styrene does not contain appropriate inhibitory compounds, for industrial production peroxides are used as initiators to create very active free radicals according to three principles: In bulk, the reactor contains only the styrene and the initiator, being exothermic, the temperature is controlled and maintained between 50 ° C and 150 ° C. In suspension, the styrene is kept in suspension in water by continuous agitation, then the initiator is added, which causes the polymerization of the styrene drops in emulsion, the styrene is maintained in emulsion in water through suitable surfactant products. | ||||||||
| PS Applications | ||||||||
Additionally, due to its high transmission of visible light and low opacity is highly appreciated in applications that require great transparency. Home appliances; refrigerators, air conditioners, ovens, microwaves, vacuum cleaners, blenders, these and other devices are often made with polystyrene (solid foam), because it is inert (does not react with other materials), economical and long durata.Settore automotive; Polystyrene (solid and foam) is used to make many auto parts, including knobs, dashboards, moldings, absorbent energy panels and foam that absorbs sound. Styrofoam is also widely used in protezione seats. Electronics; polystyrene is used for housing and other parts for televisions, computers and all kinds of equipment, in which the combination of form, function and aesthetics are essential, catering service, packaging polystyrene typically better island restoration, keeps food fresh for longer and costs less than the alternative.Isolamento; Lightweight foam polystyrene offers excellent thermal insulation in many applications, such as building walls and ceilings, refrigerators and freezers, and industrial refrigeration systems. Polystyrene insulation is inert, durable and resistant to acqua.Medico damage; Due to its clarity and ease of sterilization, polystyrene is used for a wide range of medical applications, including tissue culture plates, test tubes, Petri dishes, diagnostic components, test boxes and medical devices. Packaging: Polystyrene (solid and foam) is widely used to protect consumer products. CD and DVD cases, peanut foam packages for shipping, food packaging, meat / poultry and egg trays are cardboard boxes typically made of polystyrene for protection against damage or deterioration. | ||||||||
