SEEPS
Thermoplastics > Styrenics
| SEEPS elastomer | ||||||||
Products range | ||||||||
| SEEPS Styrene-ethylene-ethylene-propylene-styrene copolymers En Mexpolimeros ofrecemos una vasta gama SEEPS resina y sus compuestos desarrollados de acuerdo a sus necesidades, garantizando la calidad en productos y servicio. Nuestra gama de productos incluye grados compuestos de copolímeros de bloques SEEPS están disponibles desde 3 ÷ 70 Shore A hasta 70 Shore D. XPRENE EP ha sido específicamente formulado para moldeo de uno o dos disparos y desarrolla un enlace químico cuando se moldea por inyección una variedad de sustratos de plástico. XPRENE EP se divide en una amplia gama de productos como tacto suave, expandible, resistente a altas temperatura, baja deformación por compresión, FR sin halógeno y muchas otras categorías de especialidad. XPRENE EP elastómeros termoplásticos son de flujo libre y configurables. La clase XPRENE EP está formada por productos que pueden reemplazar al caucho natural y TPV (termoplástico vulcanizado). |  | |||||||
| SEEPS thermoplastic | ||||||||
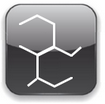
In terms of structure SEEPS are a series of hydrogenated styrenic block copolymers (HSBC) based on the elastomers is a hydrogenated isoprene, also known as Styrene-Ethylene-Ethylene / Propylene-Styrene (SEEPS) thermoplastic elastomers, with hard base blocks of styrene and a soft block based on diene, which has properties similar to rubber in a wide range of temperatures and hardness. The structure of SEEPS termoplastico is similar to the structures of SBS and SEBS, except the soft block and are high-performance thermoplastic elastomers. There is a variety of SEEPS resin qualities, from low styrene (soft) to high styrene (rigid) content, from low molecular weight (high flow) to high molecular weight (more rubber-light properties) and also different structures of soft blocks (ethylene propylene (EP), ethylene butylene (EB) and ethylene ethylene propylene (EEP)). Using synthetic technologies offers a variety of qualities, from low styrene (soft) to high styrene (rigid) content, and low molecular weight (high flow) to high molecular weight (more rubber-like properties). Also, in terms of flexible block structure, there are three different types, SEPS, SEBS and SEEPS. Regarding the structure of the blocks, the SEBS is the most popular type among the hydrogenated styrenic block copolymers. |  | |||||||
| MW molecular weight | ||||||||
A wide spectrum of products is available from high to high and ultra-high molecular weight grades, as well as grades for dynamic cross-linking. The crosslinking takes place in the central elastic block and the rigid end block, giving rise to previously unattainable properties. Compared with the standard grades of high molecular weight the very high molecular weight grades show better compression. In addition, in the manufacture of compounds, even the low molecular weight process oil can be used to maintain moderate properties similar to rubber, although the high molecular weight process oil is recommended for standard grades of high molecular weight. Those advantages of super high weight grades become more evident at higher temperatures. The improvement of the tensile strength of the SEEPS, with respect to the SEBS, is also evident in the compound with polypropylene PP and oil. The SEEPS elastomer has a greater resistance to ozone and a lower content of gels and a better abrasion. Another hallmark of the SEEPS elastomer is its better ability to treat paraffinic oil, less evaporation and oil migration compared to SEBS. This ability to treat paraffinic oil refers to the maximum amount that can be absorbed without creating an oil phase. The viscoelastic properties of mixtures of paraffinic oils with SEEPS pellets change with the content and MW molecular weight of the oil. | ||||||||
Symbols | ||||||||
| | |||||||
Properties | ||||||||
| ||||||||
| SEBS advantages over SEPS | ||||||||
|  | |||||||
Physica and mechanical properties | ||||||||
SEEPS polymer styrenic block copolymer elastomers are some of the most versatile and easy to process materials in the plastics industry. The XPRENE EP offers an excellent coefficient of surface friction, low permanent deformation, high tensile strength. While SEBS is a famous type of hydrogenated styrenic thermoplastic elastomer on the market, SEEPS is a more special grade type. Although it is a block of non-crystalline rubber, SEEPS exhibit an improvement in tensile strength compared to SEBS and SEPS due to the development of crystallinity in stretches. Also in comparison with SEBS, the SEEPS has other advantages, such as better oil retention properties, smoother, higher polyethylene affinity and better high temperature properties. SEEPS thermoplastic can be applied to the static purpose compared to SBS and has excellent performance of rubber without vulcanization. It is well accepted that viscoelasticity is an important factor in determining the processing and final properties of these materials. Each block in these copolymers that has a particular relaxation behavior results in its complex relaxation behavior. ABA type polystyrene block copolymers, such as SBS, SEBS, exhibit fast and slow relaxation processes respectively. The first corresponds to the relaxation behavior of the hard block (PS), while the second shows the relaxation behavior of randomness. | ||||||||
SEEPS Thermal properties | ||||||||
It is well known that the tensile strength and modulus of styrene- [ethylene- (ethylene-propylene)] -styrene block copolymer (SEEPS) is greater than that of styrene-butadiene-styrene block copolymer (SBS) and neither Automatic decomposition occurs beyond the glass transition temperature (Tg) of polystyrene (PS) or under extrinsic mechanical resistance, due to the existence of an intrinsic bond energy considerably high in its molecular structure. The mixtures of SEEPS polymer have improved aging properties, even after 1000 hours at 120 ° C, the compression set of un-annealed materials is only 40%. When annealing at 120 ° C for 24 h, the values can be further improved. The glass transition temperature (Tg) of the Poly (ethylene-ethylene-co-propylene) EEP blocks is typically -60 ° C, while the Tg of the polystyrene blocks is + 100 ° C. Therefore, at any temperature between -90 ° C and + 100 ° C, SEEPS will act as a physically cross-linked elastomer. Its Tg is -32 ° C slightly higher than the SEBS -55 ° C, but with respect to the SEBS it maintains better properties at low temperature. The operating temperature is guaranteed from -30 ° C to + 100 ° C. On the other hand, the high elasticity of the rubber at room temperature and the fluidity of the resin at high temperature of SEEPS are equipped with wider applications than those of the linear SBS and star in common use. | ||||||||
| SEEPS Electrical Properties | ||||||||
SEEPS are usually good insulators with a relatively high electrical resistivity, with non-polar insulators being better than polar ones. However, the electrical properties of the XPRENE EP compounds are more dependent on the ingredients used in the formulation than on the base elastomer. We make ESEPS antistatic and even conductive by the incorporation of sufficient quantities of graphite, special types of carbon black, certain metallic powders or polar products within the rubber mixture. However, the conductivity obtained by these means does not resemble that of metals. | ||||||||
| SEEPS Optical Properties | ||||||||
| One of the characteristics of a two-phase system is that the light disperses when passing from one phase to another, resulting in different levels of light transmission, in the case of SEEPS granules, we also have transparent grades. | ||||||||
| SEEPS Chemical properties | ||||||||
Unlike SBS, SEEPS does not contain double bonds (which by their nature are sensitive to oxidation), which makes it particularly resistant to wear. Therefore, it is ideal for extreme conditions that have to do with heat, ultraviolet radiation, ozone or oxidizing agents. The SEEPS resist cracking stress (acid cracking) to acids, hydroxides, methanol and ethanol, absorb oil, fats, aliphatic hydrocarbons. On the other hand, they do not resist polar hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, carboxylic acid, gasoline, ASTM oil No. 1 waxed, ASTM Aromatic No. 3 oil, toluene and benzene. | ||||||||
| SEEPS Processability | ||||||||
The SEEPS belong to the class of thermoplastic elastomers that possess the mechanical properties of rubber at room temperature and the processing capabilities of thermoplastics. The SEEPS are similar to rubber without being cross-linked, so it is easy to process them to achieve useful shapes, usually it is processed more or less at 150-230 ° C. The SEEPS can present different characteristics, mainly highlighting its great versatility for bi-injection or overmolding with plastic materials. They can be processed with several methods, such as injection, extrusion or blowing. In addition, XPRENE EP has been created especially for marketing demands and meet customer requirements. Normally they do not require drying, they have wide processing latitudes and they have good to excellent thermal stability. Process In addition, SEEPS can be processed as thermoplastics and their leftover materials can maintain the original processing and mechanical properties and can be used cyclically. The SEEPS copolymer blocks exhibit a more particular relaxation behavior in comparison with the usual homopolymers. | ||||||||
| SEEPS overmolding - 2K | ||||||||
Adhesion to a wide range of polar and non-polar substrates such as PP, PA, ABS, PC, PS, SAN, ASA, PBT, PET, ABS / PC etc. It also has a very good adhesion to PE compared to SEBS and SEPS. For the selection of the over-molding process or 2K in certain TPEs the bond strength in the application can vary, for example if the multi-shot molding process is chosen compared to insert molding, the first promotes some greater bond strength or union because the two materials in the molten state when joining, while the second gives a poor bond because one of the two materials (plastic) is superimposed on the other that is not fused (metal). So the selection of the process to be applied is a key factor to produce a high quality product. In matter of the selection of the material, it depends on the company and the product that it handles, where the characteristics of each material have to be considered for the application of the overmolding, since there are a great variety of materials that have different properties that give softness, texture, adhesion, and wall thickness of the material. In the case of the thickness effect it is necessary to know the hardness of the material, for example when you have a TPE material with low thickness (typically> 1mm) it would feel harder and vice versa when you have a thickness greater than 1mm you will feel soft. To ensure a good bond in over-molding, you are looking for a thickness in the 1.5mm range for most over-molding applications. |  | |||||||
SEEPS Polimerization | ||||||||
The SEEPS copolymer is a polyhydrogenated block copolymer (styrene-b-isoprene / butadiene-b-styrene), also called triblock copolymers, is a high molecular weight elastomer is similar to SEBS. SEEPS is produced by styrene hydrogenation / 50% by weight of butadiene / 50% by weight of isoprene / styrene triblock copolymers. The styrene MW content in this finished product varies to around 30%. Taking SEBS as an example (the most common commercial product), the butadiene monomer can be polymerized through the 1,4 or 1,2 double bonds. To have an amorphous elastic chain segment, the level of crystallinity present must be minimized. In the case of SEEPS, this is relatively easy since the hydrogenation of the isoprene segment essentially produces an alternating sequence of ethylene and propylene with small regular side branches that inhibit chain crystallization. For SEBS, the case is more complex, since the polymerization can proceed through 1.4 and 1.2 double | ||||||||
| SEEPS Compound | ||||||||
The products of the XPRENE EP class are formulated from SEEPS, oil, polypropylene, additives, and some grades have reinforcements of a continuous phase morphology. The inclusion of a charge to a polymeric matrix can describe a compatibilization effect between immiscible or immiscible mixtures and thus also exhibit excellent electrical conductivity, hardness, rigidity, mechanical and thermal resistance, and even to provide bactericidal properties to the new material. The polymer melt mixture has been the fast track for the design of new resins that seek to combine the properties of SEEPS and PP, to reach the superiority of certain characteristics due to the synergy that they can present. Unlike SBS, SEEPS does not contain double bonds (which by their nature are sensitive to oxidation), which makes it particularly resistant to wear. |  | |||||||
| SEEPS good alternative PVC | ||||||||
However, there are two main drivers in the search for PVC alternatives. First, plasticized PVC has an unwanted environmental impact related to the release of dioxins when it is incinerated uncontrolled. Second, there is a concern that PVC plasticizers (so-called "estrogen mimics") may migrate into the human body. Potential Alternatives for Plasticized PVC tubes are polymeric compositions containing polypropylene (PP) in combination with an elastomeric block copolymer. These compositions do not contain "estrogen mimics" or release dioxins when they are incinerated. SBCs are thermoplastic elastomers consisting of polystyrene end blocks (PS) chemically bonded by a central block of rubber PB. The intermediate rubber block is most frequently composed of polybutadiene PB, polyisoprene IR or its hydrogenated poly-olefinic versions: ethylene-butylene and ethylene-propylene SEEPS. | ||||||||
| SEEPS good alternative PVC medical | ||||||||
A new family of hydrogenated SBCs seems to be closing the performance gap with plasticized PVC. This family is based on intermediate blocks of improved rubber segment (ERS), which contain a higher butylene content than the more traditional intermediate SEBS blocks. The benefits of ERS-SEBS polymers include greater processing capacity and better compatibility with polypropylene. The fine network of the ERS-SEBS mixture leads to a significant improvement in transparency. Another effect of improved compatibility with PP is a widening of the glass transition temperature (Tg) below room temperature. Improved compatibility opens a series of material properties, which makes the SBC-PP mixes very suitable for the replacement of plasticized PVC. Bonding to these new materials can be a challenge due to the lack of linkable molecules along the surface of the polymer. A light-curable adhesive provides high adhesion to all the various components. High-performance polymers are often selected for applications that require structural and dimensional integrity retention under exposure to aggressive chemical conditions and elevated temperatures. One of these options for cost-effective performance polymers is plasticized PVC. However, much attention has been paid to the evaluation of more environmentally friendly and biological polymers. Styrene-ethylenebutylene-styrene copolymer rubbers (SEBS), mixtures of SEBS / polypropylene, TPE (thermoplastic elastomers) and polypropylenes are emerging as high-performance alternatives. In particular, TPEs are used to replace low durometer plasticized PVC in medical device applications, where biocompatibility characteristics are crucial. However, adhesive bonding to these polymers can be a challenge. SEEPS has been replacing the application of PVC in industries such as medical, pharmaceutical, adhesives and sealants, cables and wires, construction materials, cosmetics and personal care, agriculture, packaging, footwear, furniture, clothing, toys, sporting goods and electronics. gadgets The use of SEBS is increasing in the manufacture of medical devices, tubes and bags, since it is biocompatible and comparatively more respectful with the environment than PVC. | ||||||||
| SEEPS applications | ||||||||
These products are used mainly in construction, in addition to industrial footwear, products of the automotive industry, etc. Typical applications are profiles, household items, handles, knives, handles, accessories, feet, storage, non-slip inserts, knobs, buttons, seals, profiles, pedal covers, power tools, cable seals , plugs and sockets, cable coverings, switches, enclosures, garden tools, knobs, shock absorbers, fins, masks, caps, terminals, non-slip. SEEPS is already used in the production of toys and can replace PVC for the production of doll heads (with hair) using rotational molding techniques, one of the most difficult PVC substitutions. The SEEPS is also used in the electrical industry for items such as flexible cables and can replace PVC. These SEBS or SEEPS blends have been specially modified for the production of hard / soft injection molded parts by 2K 2-component injection molding. Since SEBS and SEEPS are not polar, an appropriate modification must be made. SEEPS is used as a possible replacement for PVC in the manufacture of toys. SEBS is similar to natural rubber and is less dangerous compared to its counterparts. The approvals of the FDA and BGW for the application of SEEPS can create an opportunity of growth for the product in the global market. A styrene-ethylene-ethylene-propylene-styrene high molecular weight block copolymer (SEEPS) is used in 20 elastic components of the diaper structure. It is used to prepare gels (gel compounds for cushions, gel pads, etc.), adhesives (Hot Melt, Solution), modifier for plastics such as Polyolefin, stenenic polymers, compatibilizer for polymer alloys, modifier for thermosetting resins. This advanced development of SEEPS keeps the characteristics extremely soft and similar to rubber, but at the same time incorporates an improvement in terms of weather resistance, temperature and chemistry. SEEPS is an interesting alternative to the TPV since it has the same type of weather resistance, shock absorbers, fins, masks, caps, terminals, anti-slip and boots. The SEEPS is also used in the electrical industry for items such as flexible cables and can replace PVC. In particular, TPEs are used to replace low durometer plasticized PVC in medical device applications, where biocompatibility characteristics are crucial. However, adhesive bonding to these polymers can be a challenge. High-performance polymers are often selected for applications that require structural and dimensional integrity retention under exposure to aggressive chemical conditions and elevated temperatures. One of these options for cost-effective performance polymers is plasticized PVC. However, much attention has been paid to the evaluation of more environmentally friendly and biological polymers. Styrene-ethylenebutylene-styrene copolymer rubbers (SEBS), mixtures of SEBS / polypropylene, TPE (thermoplastic elastomers) and polypropylenes are emerging as high-performance alternatives. | ||||||||





